前端缓存
强缓存
浏览器始终去缓存中取数据,如果有。
Cache-Control 通用消息头字段被用于在 http 请求和响应中通过指定指令来实现缓存机制。缓存指令是单向的, 这意味着在请求设置的指令,在响应中不一定包含相同的指令
使用
Cache-Control: public, max-age=<seconds> 表示在 seconds 秒内再次访问该资源,均使用本地的缓存
public
- 表明响应可以被任何对象(包括:发送请求的客户端,代理服务器,等等)缓存,即使是通常不可缓存的内容。(例如:1.该响应没有
max-age指令或Expires消息头;2. 该响应对应的请求方法是 POST 。)
- 表明响应可以被任何对象(包括:发送请求的客户端,代理服务器,等等)缓存,即使是通常不可缓存的内容。(例如:1.该响应没有
private
- 表明响应只能被单个用户缓存,不能作为共享缓存(即代理服务器不能缓存它)。私有缓存可以缓存响应内容,比如:对应用户的本地浏览器。
no-cache
- 在发布缓存副本之前,强制要求缓存把请求提交给原始服务器进行验证(协商缓存验证)。
no-store
- 缓存不应存储有关客户端请求或服务器响应的任何内容,即不使用任何缓存
Expire 是 HTTP1.0 标准下的字段,可以忽略了
Cache-Control:MDN
验证
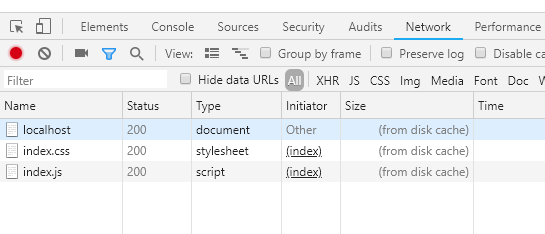
chrome 打开新标签页,输入网址回车,首页也会命中强缓存,如下图
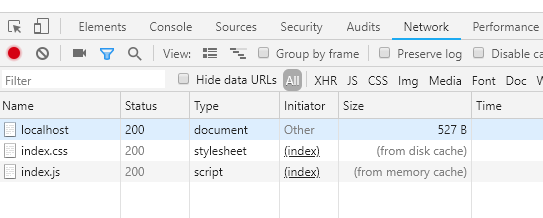
如果是当前页 F5 或者地址栏回车,首页不会命中强缓存,为什么???
协商缓存
向服务器验证一下缓存的有效性来确定是否使用缓存,两种方式
Last-Modified
可能文件内容没有什么变化,但修改时间变了,导致重新下载资源
Response Headers:服务端告诉客户端资源的最后修改时间
再此请求客户端携带以下参数到服务端
if-Modified-Since 是否文件被修改了,带上服务器给的Last-Modified
if-Unmodified-Since 是否文件没有被修改,带上服务器给的Last-Modified
Etag
算法服务器决定,hash,文件大小,等,过于复杂消耗服务器资源
Response Headers:服务端告诉客户端资源的唯一标识
在此请求客户端携带以下参数到服务端
If-None-Match 如果不匹配
Etag 优先级大于 Last-Modified
验证
协商缓存命中返回 304
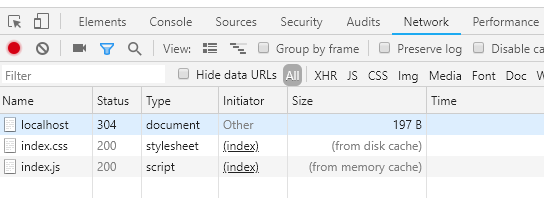
两类缓存机制可以同时存在,强制缓存的优先级高于协商缓存
示例代码
nodejs 做服务端,示例主要参考:https://github.com/BlackGoldTeam/cache-control-nodejs-demo/blob/master/server.js
const http = require('http');
const fs = require('fs');
const url = require('url');
const path = require('path');
const etag = require('etag');
const fresh = require('fresh');
const server = http.createServer(function(req, res) {
let filePath, isHtml, isFresh;
const pathname = url.parse(req.url, true).pathname;
//根据请求路径取文件绝对路径
if (pathname === '/') {
filePath = path.join(__dirname, '/index.html');
isHtml = true;
} else {
filePath = path.join(__dirname, pathname);
isHtml = false;
}
// 读取文件描述信息,用于计算etag及设置Last-Modified
fs.stat(filePath, function(err, stat) {
if (err) {
res.writeHead(404, 'not found');
res.end('<h1>404 Not Found</h1>');
} else {
if (isHtml) {
// html文件使用协商缓存
const lastModified = stat.mtime.toUTCString();
const fileEtag = etag(stat);
res.setHeader('Cache-Control', 'public, max-age=0');
res.setHeader('Last-Modified', lastModified);
res.setHeader('ETag', fileEtag);
// 根据请求头判断缓存是否是最新的
isFresh = fresh(req.headers, {
etag: fileEtag,
'last-modified': lastModified,
});
} else {
// 其他静态资源使用强缓存
res.setHeader('Cache-Control', 'max-age=10');
}
fs.readFile(filePath, 'utf-8', function(err, fileContent) {
if (err) {
res.writeHead(404, 'not found');
res.end('<h1>404 Not Found</h1>');
} else {
if (isHtml && isFresh) {
//如果缓存是最新的 则返回304状态码
//由于其他资源使用了强缓存 所以不会出现304
res.writeHead(304, 'Not Modified');
} else {
res.write(fileContent, 'utf-8');
}
res.end();
}
});
}
});
});
server.listen(8080);
console.log('server is running on http://localhost:8080/');reference
HTTP 缓存:Google Developers
HTTP 缓存:MDN

 鄂公网安备 42011502001402号
鄂公网安备 42011502001402号