JavaScript 数据类型
一、数据类型
变量是没有类型的,只有值才有。变量可以随时持有任何类型的值
基本类型(值类型或者原始类型):Number、Boolean、String、Null、Undefined、Symbol(ES6)
复杂类型(引用类型):Object(Array、Function、Date 等)
| 分类 | 类型 | 内存中的位置 |
|---|---|---|
| 基本类型 | number、boolean、string、null、undefined、symbol(ES6) | 栈(stack) |
| 引用类型 | Object(Array、Function、Date 等) | 堆(heap) |
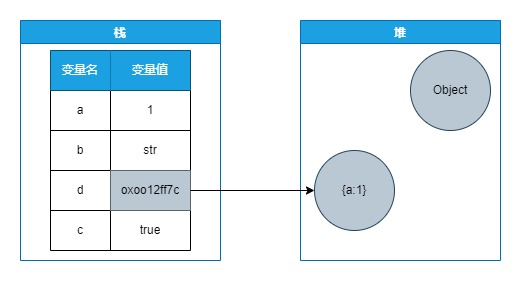
栈内存:栈的优势是,存取速度比堆要快,仅次于寄存器,栈数据可以共享。但缺点是,存在栈中的数据大小与生存期必须是确定的,缺乏灵活性。栈中主要存放一些基本类型的变量(,int, short, long, byte, float, double, boolean, char)和对象句柄。栈有一个很重要的特殊性,就是存在栈中的数据可以共享。
堆内存:堆允许程序在运行时动态地申请某个大小的内存空间。
BUILTIN_OBJECT
Function, RegExp, Date, Error, CanvasGradient, CanvasPattern, Image, Canvas
TYPED_ARRAY
Int8Array, Uint8Array, Uint8ClampedArray, Int16Array, Uint16Array, Int32Array, Uint32Array, Float32Array, Float64Array
对象
对象的属性插入次序在遍历时是可预测的
- 先遍历所有数字键(integer keys),按照升序排序
- 然后遍历所有字符串键,按照它们被添加到对象中的顺序
- 最后遍历所有Symbol键,按照它们被添加到对象中的顺序
const s1 = Symbol('1')
const s2 = Symbol('2')
const obj = {
"b": 1,
"2": 2,
[s2]: 's2',
"a": 3,
1: 4,
[s1]: 's1',
"c": 5
};
Reflect.ownKeys(obj) // ['1', '2', 'b', 'a', 'c', Symbol(2), Symbol(1)]
// for in, Object.keys 不列举 Symbol 键
for (let i in obj) {
console.log(i, obj[i]);
}1、bool
假值
"",0,-0,NaN,null,undefined,false
2、undefined
undefined 类型只有一个值,称为 undefined。 任何没有被赋值的变量的值都是未定义的。
- 值未定义
- 全局对象的一个属性,实际上是一个不允许修改的常量
{ [[Writable]]: false, [[Enumerable]]: false, [[Configurable]]: false } - undefined不是保留字
- void 0 === undefined
- 值派生自null,undefined == null
undeclared:未声明
var a;
a; // undefined
b; // ReferenceError: b is not defined'undefined' in window
Object.getOwnPropertyDescriptor(window, 'undefined')3、null
- 不是全局对象的一个属性
'null' in window - 表示缺少的标识,指示变量未指向任何对象,空对象的指针
4、undefined与null
Number(null) // 0
Number(undefined) // NaNnull表示对象不应该有值
- 作为函数的参数,表示该函数的参数不是对象。
- 作为对象原型链的终点。
- 对象置为“空”应该赋值null,这样也契合
typeof null
Object.getPrototypeOf(Object.prototype) // null
Object.create(null)undefined表示变量应该有一个值,但是还没有定义
- 变量被声明了,但没有赋值时,就等于undefined。
- 调用函数时,应该提供的参数没有提供,该参数等于undefined。
- 对象没有赋值的属性,该属性的值为undefined。
- 函数没有返回值时,默认返回undefined。
- 非对象置为“空”应该赋值undefined
var i;
i // undefined
function f(x){console.log(x)}
f() // undefined
var o = new Object();
o.p // undefined
var x = f();
x // undefined包装类型
String Boolean Number
Number
- 0 除以0会返回
NaN,但是其他数除以0则不会返回NaN,返回Infinity
双精度64位浮点数 遵循ieee 754标准
- 对于十进制,小数点的左移右移相当于乘以10或除以10
- 对于二进制,小数点的左移右移相当于乘以2或除以2
科学计数法
- 节省内存空间
- 直观的确定大小
二进制科学计数法
- 指数基数为2
- n为整数
IEEE 754定义
https://zh.wikipedia.org/zh-hans/IEEE_754
- sign:0表示正数,1表示负数
- exponent: 指数值加上一个偏移值,偏移值为:
,其中的n为存储指数的比特位长度 - fraction:小数部分(最高位1规定不显示存储)
32位单精度
- 1位符号位,8位指数位,23位小数位;偏移值127
64位:1 11 52
举例
sign为0,exponent为6+127=133=
,fraction为001110 0-10000101-00111000000000000000000
sign为1,exponent为
,fraction为0000 1-10000011-00000000000000000000000
sign为0,exponent为
,fraction为0000 0-10000001-11110000000000000000000
还原0.1+0.2
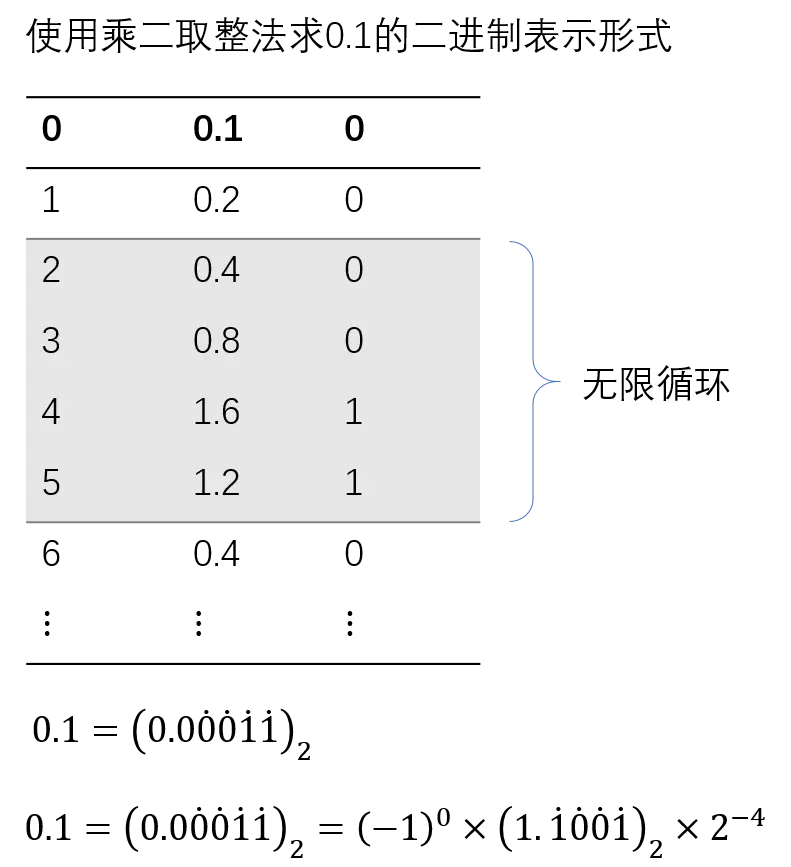
sign为0,exponent为
,fraction为0000 0-01111011-10011001100110011001101
sign为0,exponent为
,fraction为0000 0-01111100-10011001100110011001101
先进行“对位”,将较小的指数化为较大的指数,并将小数部分相应右移
- 零舍一入
// 0.3 64位 0.0100110011001100110011001100110011001100110011001101
// 0.3 32位 0.0100110011001100110011010
const str = '0.0100110011001100110011001100110011001100110011001101',
len = str.length
let e = 0,
expression = ''
for (let i = 0; i < len; i++) {
const element = str[i]
if (element === '.') {
continue
}
expression += element + ' * 2 ** ' + e-- + (i === len - 1 ? '' : ' + ')
}
console.log(expression)
console.log(eval(expression))reference
https://segmentfault.com/a/1190000008268668
https://babbage.cs.qc.cuny.edu/IEEE-754/
https://devtool.tech/double-type
解决方案
https://github.com/josdejong/mathjs
https://github.com/nefe/number-precision
Map,WeakMap
WeakMap:其中的键是弱引用的。其键必须是对象,而值可以是任意的
node --expose-gc server.js
global.gc()
console.log('start:heapUsed', process.memoryUsage().heapUsed)
let key = new Array(5 * 1024 * 1024).fill(1)
console.log('array:heapUsed', process.memoryUsage().heapUsed)
const map = new Map()
map.set(key, 1)
global.gc()
console.log('map :heapUsed', process.memoryUsage().heapUsed)
key = null
global.gc()
console.log('null :heapUsed', process.memoryUsage().heapUsed)二、类型检测
1、typeof
安全:未声明的返回 undefined (TDZ)返回一个字符串,表示未经计算的操作数的类型
// 数值
typeof Math.LN2 === 'number'
typeof Infinity === 'number'
typeof NaN === 'number' // 尽管它是 "Not-A-Number" (非数值) 的缩写
typeof Number(1) === 'number' // Number 会尝试把参数解析成数值
typeof 42n === 'bigint'
// 字符串
typeof `template literal` === 'string'
typeof String(1) === 'string' // String 将任意值转换为字符串,比 toString 更安全
// 布尔值
typeof Boolean(1) === 'boolean' // Boolean() 会基于参数是真值还是虚值进行转换
typeof !!1 === 'boolean' // 两次调用 ! (逻辑非) 操作符相当于 Boolean()
// Symbols
typeof Symbol() === 'symbol'
typeof Symbol('foo') === 'symbol'
typeof Symbol.iterator === 'symbol'
// Undefined
typeof undefined === 'undefined'
typeof declaredButUndefinedVariable === 'undefined'
typeof undeclaredVariable === 'undefined'
// 对象
typeof { a: 1 } === 'object'
// 使用 Array.isArray 或者 Object.prototype.toString.call
// 区分数组和普通对象
typeof [1, 2, 4] === 'object'
typeof new Date() === 'object'
typeof /regex/ === 'object' // 历史结果请参阅正则表达式部分
// 下面的例子令人迷惑,非常危险,没有用处。避免使用它们。
typeof new Boolean(true) === 'object'
typeof new Number(1) === 'object'
typeof new String('abc') === 'object'
// 函数
typeof function() {} === 'function'
typeof class C {} === 'function'
typeof Math.sin === 'function'除 Function 外的所有构造函数的类型都是
objecttypeof new Objecttypeof new Function
typeof null === "object"typeof document.all === 'undefined';
// Opera 中`document.attachEvent`(未验证)
// for “modern” browsers
typeof document.all // 'undefined'
document.all == undefined // true
Object.prototype.toString.call(document.all) // '[object HTMLAllCollection]'
// for ancient browsers eg ie <= 10
typeof document.all // 'object'
document.all == undefined // false
Object.prototype.toString.call(document.all) // '[object HTMLAllCollection]'
if (document.all) {
// code that uses `document.all`, for ancient browsers
} else if (document.getElementById) {
// code that uses `document.getElementById`, for “modern” browsers
}- 在其被声明之前对块中的
let和const变量使用typeof会抛出一个 ReferenceError
2、instanceof
用于检测构造函数的 prototype 属性是否出现在某个实例对象的原型链上。
;[] instanceof Array // true
;[] instanceof Object // true3、Object.prototype.toString()
表示该对象的字符串,在toString方法被调用时,会执行下面的操作步骤:
如果this的值为undefined,则返回
"[object Undefined]".如果this的值为null,则返回
"[object Null]".让let O成为调用 ToObject(**this)**的结果.
让class成为O的内部属性[[Class]]的值.
返回三个字符串**"[object , class ]**
Object.prototype.toString.call('An') // "[object String]"
Object.prototype.toString.call(1) // "[object Number]"
Object.prototype.toString.call(Symbol(1)) // "[object Symbol]"
Object.prototype.toString.call(null) // "[object Null]"
Object.prototype.toString.call(undefined) // "[object Undefined]"
Object.prototype.toString.call(function() {}) // "[object Function]"
Object.prototype.toString.call({ name: 'An' }) // "[object Object]"Object.prototype.toString.call([]).slice(8, -1) === "Array";
自定义类型 返回 object
Array.prototype.toString
问题来源
Array.prototype.toString.call({join(){ return 42 }})
探究
数组的
toString()实际调用了join()[2, 3, 4].toString() == '2,3,4'[2, 3, 4].join() === '2,3,4'- 可以通过修改原型上的
join方法,再调toString验证
Array的原型上实现了自己的toString方法,所以不会到Object的原型上去找toString
那么问题肯定就出在Array的原型上toString方法的实现
借助两大法宝:
ecma的规范:
https://tc39.es/ecma262/#sec-array.prototype.tostring
v8的实现:
// https://tc39.github.io/ecma262/#sec-array.prototype.tostring
transitioning javascript builtin ArrayPrototypeToString(
js-implicit context: NativeContext, receiver: JSAny)(...arguments): JSAny {
// 1. Let array be ? ToObject(this value).
const array: JSReceiver = ToObject_Inline(context, receiver);
// 2. Let func be ? Get(array, "join").
const prop: JSAny = GetProperty(array, 'join');
try {
// 3. If IsCallable(func) is false, let func be the intrinsic function
// %ObjProto_toString%.
const func: Callable = Cast<Callable>(prop) otherwise NotCallable;
// 4. Return ? Call(func, array).
return Call(context, func, array);
} label NotCallable {
return ObjectToString(context, array);
}
}解析
借助规范和代码,可以得到toString的实现逻辑:
- 把
toString()的参数转化为对象,例子中{join(){ return 42 }}就是一个对象,这一步得到的array就是{join(){ return 42 }} - 获取
join属性 - 把
join转为方法 join能转为方法,就调用这个方法并返回,join不能转为方法,就调用Object.prototype.toString返回
至此真相大白,关键就在于获取了join
联系到前面说的:数组的toString()实际调用了join(),也就理解toString为何这么设计了
4、 Array.isArray()
var iframe = document.createElement('iframe')
document.body.appendChild(iframe)
xArray = window.frames[window.frames.length - 1].Array
var arr = new xArray(1, 2, 3) // [1,2,3]
// Correctly checking for Array
Array.isArray(arr) // true
Object.prototype.toString.call(arr) // true
// Considered harmful, because doesn't work though iframes
arr instanceof Array // false三、类型转换
https://tc39.es/ecma262/#sec-type-conversion
ToString、ToNumber 和 ToBoolean,ToPrimitive
ToNumber 和 ToBoolean,没有暴露
ECMAScript 语言会根据需要隐式执行自动类型转换。 为了阐明某些构造的语义,定义一组转换抽象操作很有用。 转换抽象操作是多态的; 它们可以接受任何 ECMAScript 语言类型的值。 但是这些操作没有使用其他规范类型。
- BigInt 类型在 ECMAScript 语言中没有隐式转换; 程序员必须显式调用 BigInt 来转换其他类型的值。
抽象操作 ToPrimitive 接受参数输入(ECMAScript 语言值)和可选参数 preferredType(字符串或数字),并返回包含 ECMAScript 语言值的正常完成或抛出完成。 它将其输入参数转换为非对象类型。 如果一个对象能够转换为多个原始类型,它可以使用可选提示 preferredType 来支持该类型。 它在调用时执行以下步骤:
- 调用
obj[Symbol.toPrimitive](hint)如果这个方法存在, - 否则,如果 hint 是 "string"尝试调用 obj.toString() 或 obj.valueOf(),无论哪个存在。
- 否则,如果 hint 是 "number" 或者 "default"尝试调用 obj.valueOf() 或 obj.toString(),无论哪个存在。
hint的三种值:
- default
- string
- number
Date 和 Symbol 覆盖了默认的 ToPrimitive
- Symbol.prototype[Symbol.toPrimitive]
- Date.prototype[Symbol.toPrimitive]
new Date('2022-6-1') - new Date()
new Date('2022-6-1') + new Date() // defaultlet user = {
name: 'John',
money: 1000,
[Symbol.toPrimitive](hint) {
console.log(`hint: ${hint}`);
return hint == 'string' ? `{name: "${this.name}"}` : this.money;
},
};
console.log(`${user}`); // hint: string -> {name: "John"}
console.log(+user); // hint: number -> 1000
console.log(user + 500); // hint: default -> 1500 //不确定是string还是number,hint就是default- toString 方法返回一个字符串 "[object Object]"。
- valueOf 方法返回对象自身
let user = {
name: 'John',
money: 1000,
// 对于 hint="string"
toString() {
return `{name: "${this.name}"}`;
},
// 对于 hint="number" 或 "default"
valueOf() {
return this.money;
},
};
console.log(`${user}`); // toString -> {name: "John"}
console.log(+user); // valueOf -> 1000
console.log(user + 500); // valueOf -> 1500toString,valueOf必须返回一个原始值
const b = new Boolean(false);
console.log(b == b.valueOf());
console.log(b === b.valueOf());const a = +'1'; //字符串转数字
const b = !!'0' // 转布尔四、相等
https://dorey.github.io/JavaScript-Equality-Table/
非严格相等 ==
比较前,先隐式转换为相同类型,再比较两个值是否相等
| Undefined | Null | Number | String | Boolean | Object | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Undefined | true | true | false | false | false | IsFalsy(B) |
| Null | true | true | false | false | false | IsFalsy(B) |
| Number | false | false | A === B | A === ToNumber(B) | A=== ToNumber(B) | A== ToPrimitive(B) |
| String | false | false | ToNumber(A) === B | A === B | ToNumber(A) === ToNumber(B) | ToPrimitive(B) == A |
| Boolean | false | false | ToNumber(A) === B | ToNumber(A) === ToNumber(B) | A === B | ToNumber(A) == ToPrimitive(B) |
| Object | false | false | ToPrimitive(A) == B | ToPrimitive(A) == B | ToPrimitive(A) == ToNumber(B) | A === B |
- ToNumber(A) 表示尝试在比较前将参数 A 转换为数字,与+A 效果相同
- ToPrimitive(A)通过尝试调用 A 的 A.toString() 和 A.valueOf() 方法,将参数 A 转换为原始值
“看起来不符合预期”的情况:
console.log(42 == [42])
console.log('0' == false)
console.log(false == 0)
console.log(false == '')
console.log(false == [])
console.log('' == 0)
console.log('' == [])
console.log(0 == [])
console.log([] == ![])严格相等 ===
不进行隐式转换,类型相同,值也相同,就是全等
- 两个 NaN 不是全等的
- +0 和-0 是全等的
同值相等 Object.is
与===的不同
- 两个 NaN 是相等的
- +0 和-0 是不相等的
零值相等
Map,Set使用,与同值相等类似,不过认为+0 和-0 是相等的

 鄂公网安备 42011502001402号
鄂公网安备 42011502001402号